Bismuth and Tin Plating Technologies | Advint Incorporated
Recent research has unveiled groundbreaking advancements in electrodeposition techniques for bismuth and tin, offering innovative insights that could transform metal coating technologies. These studies provide crucial information on optimizing electroplating processes, enhancing coating uniformity, and understanding the impact of various factors on deposit properties.
Bismuth Electrodeposition from Perchloric Acid Solutions
A pioneering study on bismuth electrodeposition from perchloric acid solutions has revealed several key findings:
Bismuth perchlorate solutions exhibit exceptional stability, resisting hydrolysis and precipitation even when diluted.
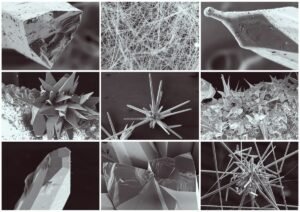
Optimal deposition conditions were achieved at room temperature using a current density of 3.1 A/dm², resulting in smooth, finely crystalline cathode deposits free of rough edges.
The ideal bath composition was determined to be 40 g/L of bismuth oxide and 104 g/L of perchloric acid, ensuring efficient deposition.
Cathodic current efficiency approached 100%, indicating minimal energy waste during the deposition process.
The deposited bismuth contained trace amounts (0.4-0.5%) of perchlorate, suggesting the need for further purification in certain applications.
While addition agents such as glue and cresol slightly improved the deposits, they were not essential for achieving satisfactory results. This method shows promise for specialized applications in electrical and magnetic devices. However, the brittleness and tarnishing tendency of the deposited bismuth currently limit its broader commercial use.
Enhancing Coating Uniformity in High-Speed Tin Plating
Another crucial study focused on improving coating homogeneity in high-speed tin electroplating:
Both 3D and simplified 2D models were developed to analyze factors affecting coating uniformity, such as electrolyte potential distribution, tin ion concentration, gas evolution, and current distribution.
The primary challenge identified was the “edge effect,” resulting in thicker coatings at the cathode edges, posing significant challenges in achieving consistent coatings.
Adjusting anode sizes or arrangements proved insufficient. However, auxiliary devices like insulating bars and auxiliary cathodes showed potential in mitigating the edge effect.
Although auxiliary cathodes nearly eliminated the edge effect, they introduced drawbacks such as increased current and tin wastage.
The simulation results correlated well with actual production data, particularly for high coating masses, though discrepancies were noted at lower coating masses.
These findings provide valuable strategies for enhancing coating uniformity in high-speed electroplating processes, applicable beyond tin plating.
Impact of Additives and Current Density on Tin Deposits
Further research explored the effects of organic plating additives and current density on the properties of electroplated tin deposits:
Increasing the concentration of organic plating additives raised the carbon content in tin deposits from 5 wt% to 8 wt%.
Higher current densities caused the tin oxide film to reach donor density saturation at lower additive concentrations, suggesting a role in the decomposition of organic additives and subsequent carbon incorporation.
Depth profile analysis revealed that carbon was consistently incorporated throughout the deposit, not just sporadically.
The native tin oxide layer exhibited n-type semiconductor characteristics, crucial for understanding its potential applications in electronic devices.
These studies highlight the complexities of electrodeposition processes and pave the way for future innovations in electroplating technologies. By optimizing bath compositions, current densities, and additive concentrations, researchers can develop more efficient and effective electroplating methods for bismuth, tin, and potentially other metals, opening new possibilities in coating technologies and electronic applications.
Conclusions
The research on bismuth from perchloric acid solutions offers a reliable method for specialized applications, while the high-speed tin plating study provides strategies for achieving uniform coatings.
Both investigations underscore the critical influence of additives and current density on the properties of electrodeposited metals, setting the stage for future advancements in electroplating technologies.
You may like also
Plastic Metamorphosis: Cutting-Edge Plating Techniques Revolutionizing Modern Manufacturing

Posted By:Venkat Raja
Jun 23, 2024
Tags: